SEO Basics: A Beginner's Guide to Boosting Your Website's Visibility

What is SEO?

Search Engine Optimization (SEO) refers to the process of optimizing your website to rank higher on search engine results pages (SERPs). The higher your site ranks, the more likely users are to visit it. SEO focuses on both the technical and creative elements required to improve rankings, drive traffic, and increase awareness in search engines.
SEO is not just about search engines; it’s also about providing the best experience for your users. When your website is optimized, it’s faster, more user-friendly, and easier to navigate, which can significantly enhance user satisfaction and encourage repeat visits.
Why is SEO important?
1. Increases Organic Traffic: SEO helps you attract users without relying on paid ads. With proper optimization, your website can rank higher and attract consistent traffic.
2. Builds Credibility: Websites that rank higher on SERPs are perceived as more trustworthy. Search engines use algorithms to reward quality and relevance, so a higher rank can boost your brand’s credibility.
3.Cost-Effective: Compared to paid campaigns, SEO provides long-term benefits with minimal ongoing costs. Once you rank well, maintaining your position is far less expensive than continuously running ads.

4. Enhances User Experience: Good SEO practices often improve website usability and speed. For instance, optimizing for mobile devices and ensuring fast page loads improve both rankings and user experience.

5. Competitive Edge: In a crowded market, effective SEO can set you apart. If your competitors are investing in SEO, staying ahead can help you capture more market share.
The Three Pillars of SEO
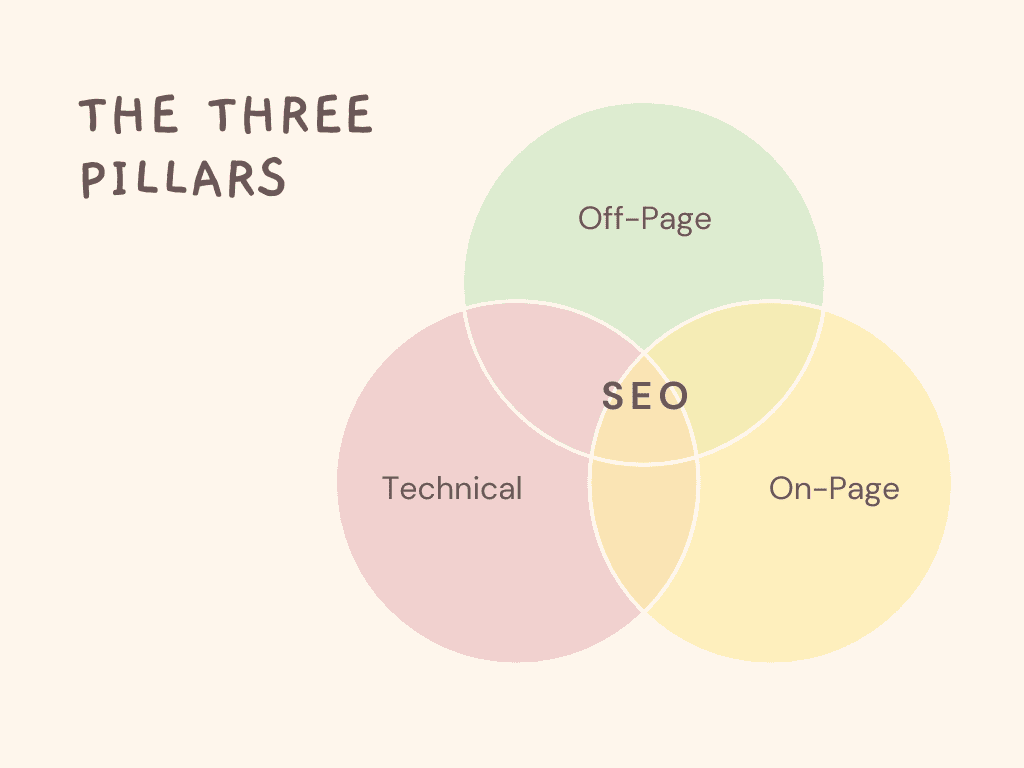
1. On-Page SEO
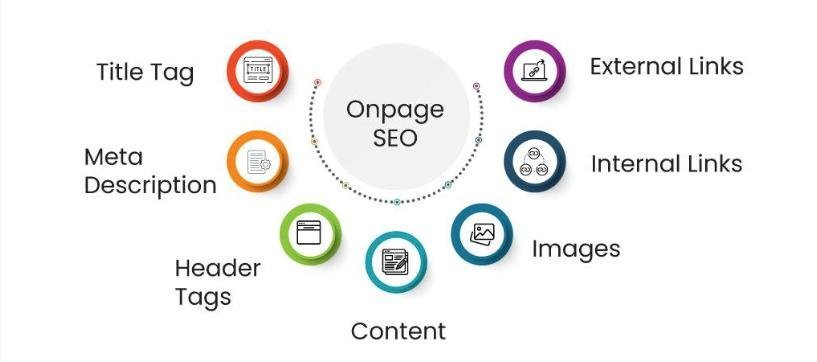
On-page SEO involves optimizing the elements within your website. Key areas to focus on include:
* Title Tags and Meta Descriptions: Use relevant keywords and keep them compelling. Title tags are often the first thing users see, so make them count.
* Content Quality: Create high-value, keyword-rich, and user-friendly content. Focus on answering user queries and solving their problems.
*URL Structure: Use clean, descriptive URLs (e.g., www.example.com/seo-basics). Avoid long, confusing URLs with random strings of numbers or characters.
* Internal Linking: Link to other pages within your site to improve navigation. This helps users discover more of your content and assists search engines in understanding your site structure.
* Image Optimization: Use descriptive file names, alt text, and compressed images to enhance load speed and accessibility. Visuals are important, but they should not slow down your website.
2. Off-Page SEO
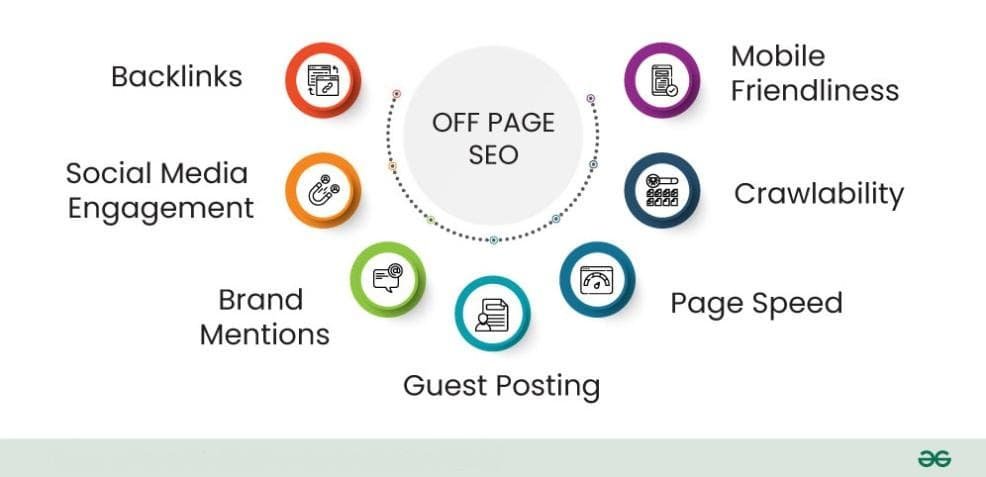
Off-page SEO refers to activities performed outside your website to improve its authority and reputation. Key strategies include:
* Backlink Building: Obtain quality backlinks from reputable sites. Backlinks act as “votes of confidence” from other sites, signaling to search engines that your content is valuable.
* Social Media Engagement: Share your content on social platforms to drive traffic. Although social media links don’t directly affect rankings, they can increase visibility and engagement.
* Guest Blogging: Publish articles on other websites to reach a broader audience. This strategy can also help establish you as an authority in your niche.
3. Technical SEO
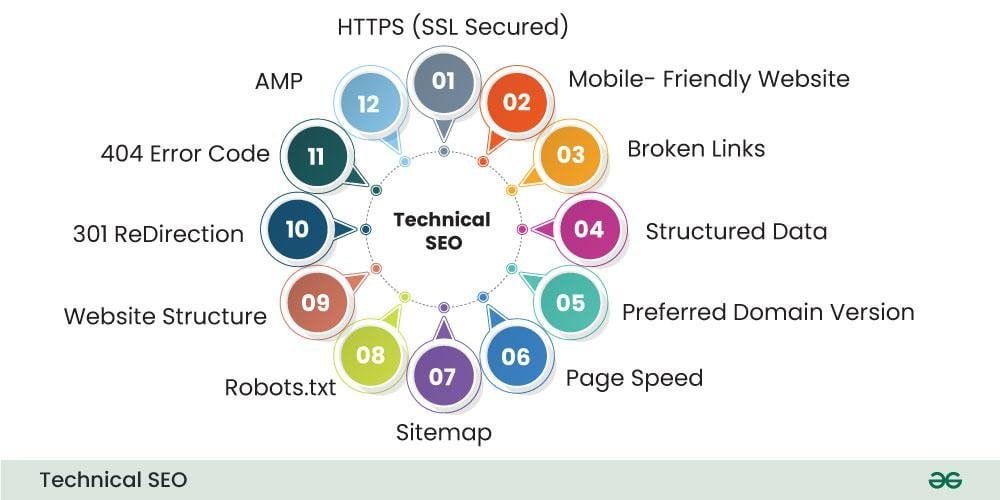
Technical SEO focuses on the backend elements of your site. Key aspects to consider are:
*Site Speed: Ensure fast loading times to reduce bounce rates. Use tools like PageSpeed Insights to identify areas for improvement.
*Mobile-Friendliness: Optimize your site for mobile devices. With Google’s mobile-first indexing, a mobile-friendly site is essential for rankings.
*Secure Connections: Use HTTPS for improved security and search engine preference. An SSL certificate not only protects data but also signals trustworthiness.
*Crawlability: Ensure search engines can crawl and index your website effectively. Submit sitemaps and use robots.txt files appropriately.
Key SEO Practices for Beginners
1. Conduct Keyword Research

Keywords are the foundation of SEO. Use tools like Google Keyword Planner, Ahrefs, or SEMrush to find relevant terms that your audience is searching for. Focus on:
* Short-Tail Keywords: General terms (e.g., “SEO basics”) that often have high search volume but are more competitive.
* Long-Tail Keywords: More specific phrases (e.g., “how to improve website SEO visibility”) that have lower search volume but higher conversion rates.
When selecting keywords, consider the user’s search intent. Are they looking for information, making a purchase decision, or seeking solutions? Align your content with their needs.
2. Create High-Quality Content

Content is king in SEO. Ensure your content is:
* Relevant: Address the needs of your target audience. Answer their questions clearly and comprehensively.
* Engaging: Use visuals, bullet points, and subheadings for better readability. Break up long blocks of text with images, videos, or infographics.
* Fresh: Regularly update your content to maintain relevance. Evergreen content with periodic updates tends to perform well over time.
3. Optimize for Mobile

4. Improve Website Speed

5. Focus on User Experience (UX)
6. Build Backlinks

High-quality backlinks signal to search engines that your site is credible. To earn backlinks:
* Create shareable content like infographics.
* Network with industry experts.
* Write guest posts for reputable websites.
* Participate in relevant online forums or communities where you can share your content.
Tools to Help You Get Started

* Google Analytics: Track website traffic and user behavior. Understanding where your visitors come from and what they do on your site can help you refine your strategy.
* Google Search Console: Monitor your site’s performance on SERPs. This tool also helps you identify technical issues like crawl errors.
* Yoast SEO (for WordPress): Optimize your blog posts and pages. Yoast provides actionable recommendations for improving SEO on individual pages.
* SEMrush or Ahrefs: Analyze keywords, competitors, and backlinks. These tools are excellent for in-depth research and strategy planning.
* GTmetrix: Test and improve your website’s speed. A faster website can significantly improve user experience and rankings.
* Screaming Frog: A website crawler that helps identify technical SEO issues like broken links or missing meta tags.
Measuring SEO Success

To gauge the effectiveness of your SEO efforts, focus on these metrics:
* Organic Traffic: Monitor the number of visitors coming from search engines. Increasing organic traffic is often the primary goal of SEO.
* Keyword Rankings: Check if your target keywords are ranking higher. Use tools like Ahrefs or SEMrush to track keyword performance.
* Bounce Rate: Aim for a low bounce rate to ensure users stay on your site. A high bounce rate may indicate that your content is not meeting user expectations.
* Backlinks: Track the number and quality of your backlinks. Tools like Moz or Majestic can help analyze your backlink profile.
Final Thoughts

